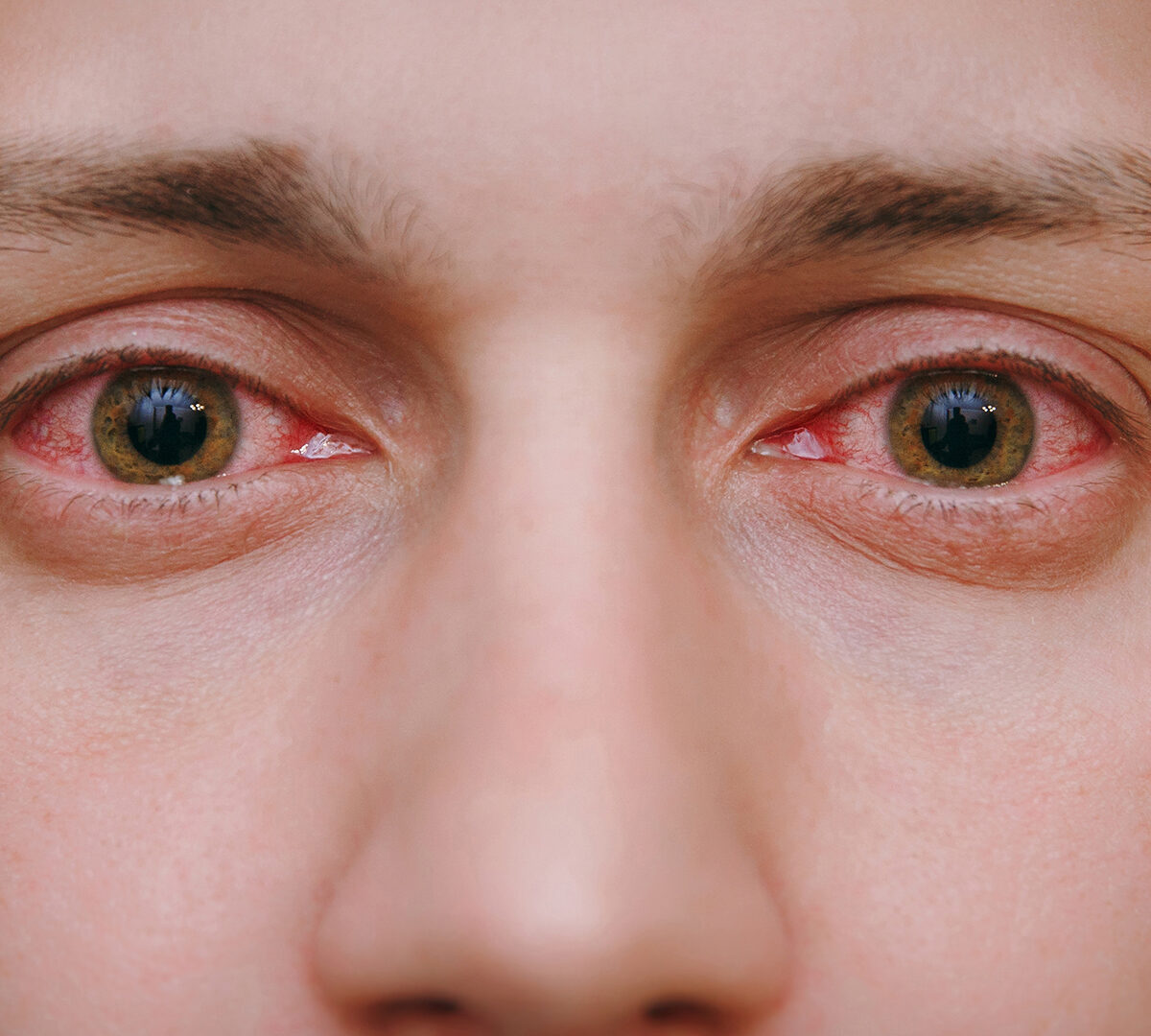
In today’s context, the recent surge of Conjunctivitis virus, also known as Ashob-e-Chashm, has garnered our attention and raised concerns throughout our nation. However, amid these challenging times, there is a silver lining – we have the ability to take control and overcome this virus. By adopting a series of informed precautions, supported by effective methods, we can protect ourselves and our communities from the grasp of Conjunctivitis. Let’s explore these strategies that hold the key to creating a healthier and safer environment for everyone.
Conjunctivitis, commonly referred to as “Pink Eye,” is a widespread eye infection that can affect individuals of all age groups. This article delves into the various facets of conjunctivitis, shedding light on its different types, signs, symptoms, methods of diagnosis, available treatments, and preventative measures. By enhancing our comprehension of conjunctivitis, we can better manage this condition and promote eye health.
Types of Conjunctivitis
Viral Conjunctivitis
Viral conjunctivitis primarily stems from viruses such as adenovirus and the herpes simplex virus. It spreads through direct contact with infected individuals, contaminated surfaces, or respiratory droplets. Common symptoms include redness, watery eyes, and itching. While viral conjunctivitis typically resolves on its own within a couple of weeks, it is crucial to maintain proper care and hygiene to prevent its transmission.
Bacterial Conjunctivitis
Bacterial conjunctivitis is caused by bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pneumoniae. It spreads through direct contact with discharge from an infected eye. Symptoms often include redness, thick yellow or green discharge, and crusting of the eyelids. Antibiotic eye drops or ointments prescribed by a healthcare professional effectively treat bacterial conjunctivitis.
Allergic Conjunctivitis
Allergic conjunctivitis results from an allergic reaction to allergens like pollen, dust mites, or pet dander. Symptoms encompass redness, itching, and excessive tearing. Managing allergic conjunctivitis involves avoiding allergens, using antihistamine eye drops, and considering immunotherapy options for relief.
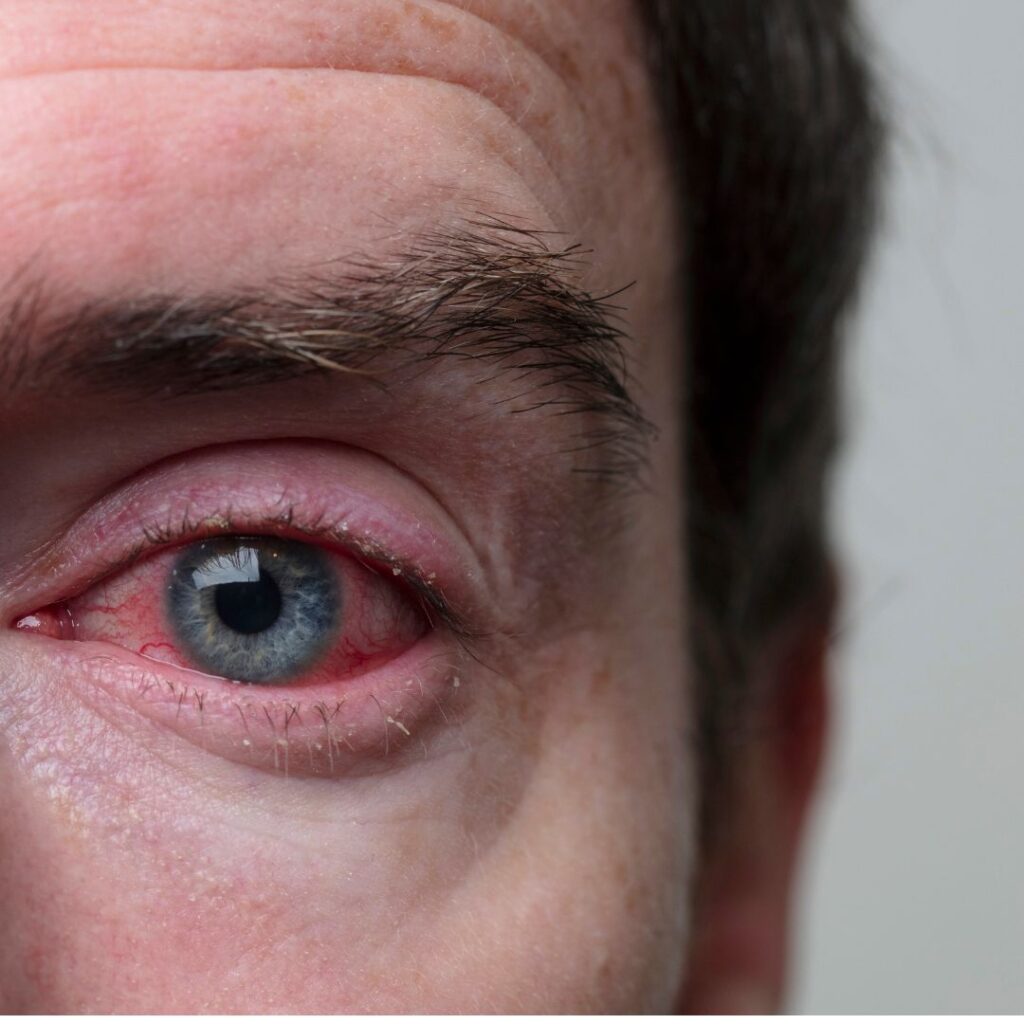
Irritant Conjunctivitis
Irritant conjunctivitis arises from exposure to irritants such as smoke, chemicals, or foreign bodies. Symptoms consist of redness, tearing, and a sensation of grittiness. To alleviate discomfort and prevent further irritation, flushing the eyes with clean water and using artificial tears are recommended.
Signs and Symptoms
Conjunctivitis presents with various signs and symptoms that may vary depending on its type. Redness and bloodshot eyes are common across all types, accompanied by distinguishing features:
- Watery or Discharge from the Eyes: Viral and bacterial conjunctivitis often lead to watery eyes, while bacterial conjunctivitis may result in thicker discharge.
- Gritty Sensation or Itchiness: Allergic conjunctivitis is characterized by intense itching and a sensation of grittiness in the eyes.
- Swelling of Conjunctiva: Swelling of the conjunctiva is a common symptom in various types, causing discomfort and altered appearance.
- Light Sensitivity and Blurred Vision: Sensitivity to light and blurred vision may occur in severe cases, particularly in viral and bacterial types.
Diagnosis of Conjunctivitis
Diagnosing conjunctivitis involves a comprehensive approach, including:
- Physical Examination: A healthcare professional examines the eyes for redness, swelling, discharge, and other characteristic symptoms.
- Patient History: Information about recent exposure to allergens, irritants, or infected individuals helps identify the type of conjunctivitis.
- Collecting Eye Discharge for Testing: In cases of bacterial conjunctivitis, collecting a sample of eye discharge can aid in identifying the causative bacteria and guiding treatment.
- Differentiating Between Types: Specific symptoms and their duration assist in distinguishing between viral, bacterial, allergic, and irritant conjunctivitis.
Preventing the Spread
Preventing the spread of conjunctivitis is essential to limit its transmission:
- Practicing Good Hygiene: Regular handwashing and avoiding touching the eyes can reduce the risk of infection.
- Avoiding Touching Eyes: Touching the eyes with unwashed hands can introduce pathogens and irritants.
- Personal Items and Conjunctivitis: Avoid sharing towels, pillows, and cosmetics to prevent the spread of infection.
- Staying Home and Contagious Period: Individuals with conjunctivitis should stay home until symptoms subside to prevent infecting others.
Home Care and Relief
Managing conjunctivitis at home involves simple yet effective strategies:
- Warm Compresses for Comfort: Applying warm compresses can alleviate discomfort and reduce swelling.
- Artificial Tears and Lubricants: Using artificial tears helps keep the eyes moist and soothes irritation.
- Cold Compresses for Soothing: Cold compresses can reduce redness and provide relief from itching.
- Over-the-Counter Medications: Non-prescription eye drops or antihistamines can help manage symptoms but should be used as directed.
When to Seek Medical Help
Knowing when to seek medical attention is crucial:
- Severity of Symptoms: If symptoms are severe, including intense pain or impaired vision, medical attention is necessary.
- Duration of Symptoms: If symptoms persist beyond a week or two, consultation with a healthcare professional is recommended.
- Underlying Health Conditions: Individuals with pre-existing eye conditions or compromised immune systems should seek prompt medical care.
- Importance of Professional Evaluation: A healthcare professional can accurately diagnose the type of conjunctivitis and recommend appropriate treatment.
Treatment Approaches
Viral Conjunctivitis Treatment
Treatment for viral conjunctivitis primarily involves supportive care:
- Supportive Care: Using artificial tears and applying cool compresses can provide relief from discomfort.
- Timeframe for Recovery: Viral conjunctivitis often resolves within two to three weeks without specific treatment.
- Avoiding Contamination: Practicing good hygiene and avoiding contact with others can prevent the spread of the virus.
Bacterial Conjunctivitis Treatment
Bacterial conjunctivitis requires a more targeted approach:
- Antibiotic Eye Drops or Ointments: A healthcare professional may prescribe antibiotic eye drops or ointments to eliminate bacterial infection.
- Following Doctor’s Instructions: Adhering to the prescribed treatment regimen and completing the course of antibiotics is crucial.
- Reevaluation and Monitoring: If symptoms persist, a follow-up with a healthcare provider ensures effective treatment.
Allergic Conjunctivitis Treatment
Managing allergic conjunctivitis involves allergy management:
- Allergen Avoidance: Identifying and minimizing exposure to allergens helps prevent allergic reactions.
- Antihistamine Eye Drops: Over-the-counter or prescription antihistamine eye drops can alleviate itching and redness.
- Immunotherapy Options: For severe cases, allergen immunotherapy can be considered to desensitize the immune system.
Irritant Conjunctivitis Treatment
Treating irritant conjunctivitis focuses on symptom relief:
- Flushing the Eyes: Flushing the eyes with clean water helps remove irritants and soothes the eyes.
- Artificial Tears for Relief: Artificial tears provide lubrication and alleviate discomfort.
- Avoiding Irritants: Identifying and avoiding irritants helps prevent recurrence.
Special Considerations for Different Groups
Conjunctivitis in Children
Managing conjunctivitis in children requires special attention:
- Child-Friendly Treatments: Using gentle techniques such as warm compresses and age-appropriate eye drops.
- School and Contagion Concerns: Children with conjunctivitis should stay home from school until symptoms clear to prevent the spreading of the infection.
- Parental Guidance: Parents should monitor symptoms, administer prescribed treatments, and seek medical help if needed.
Conjunctivitis in Adults
Addressing conjunctivitis in adults involves considering work and social interactions:
- Work and Social Interaction: Depending on the severity of symptoms, individuals may need to take time off work or limit social interactions.
- Recovery Time for Adults: Adults often recover within a couple of weeks, with proper care and adherence to treatment.
- Preventive Measures: Practicing good hygiene and avoiding close contact with infected individuals reduce the risk of contracting conjunctivitis.
Conjunctivitis in Elderly Individuals
Managing conjunctivitis in the elderly requires additional considerations:
- Age-Related Factors: Age-related changes in the eyes can contribute to increased susceptibility to infections.
- Managing Discomfort: Elderly individuals may experience more discomfort; therefore, careful symptom management is important.
- Caretaker Role: Caretakers should provide support in adhering to treatment plans and maintaining good eye hygiene.
Complications and Risks
Understanding potential complications is essential:
- Spreading to Other Eye: If one eye is infected, taking precautions to prevent the infection from spreading to the other eye is vital.
- Secondary Infections: Without proper treatment, conjunctivitis can lead to secondary bacterial infections.
- Corneal Involvement: In severe cases, conjunctivitis can affect the cornea, potentially causing vision problems.
- Scarring and Lasting Effects: Untreated conjunctivitis can lead to scarring and lasting damage to the conjunctiva.
Frequently Asked Questions
Addressing common queries about conjunctivitis:
- Can Conjunctivitis Go Away on Its Own? Viral conjunctivitis can resolve without treatment, but other types may require medical intervention.
- Is Conjunctivitis Contagious? Yes, conjunctivitis is contagious, particularly viral and bacterial types.
- Can I Wear Contact Lenses? It’s advisable to avoid wearing contact lenses while experiencing conjunctivitis to prevent worsening the condition.
- When Can I Return to Work or School? Wait until symptoms have cleared and your doctor confirms it’s safe to return to prevent spreading the infection.
- How Can I Soothe Itchy Eyes? Using cool compresses and artificial tears can help soothe itching and discomfort.
Conclusion
In conclusion, conjunctivitis, commonly known as “Pink Eye,” is a multifaceted eye infection that can impact individuals of all ages. By understanding its types, symptoms, treatment options, and preventative measures, we can take proactive steps to manage conjunctivitis effectively. Timely intervention, professional guidance, and raising awareness about conjunctivitis are essential for promoting eye health and overall well-being.