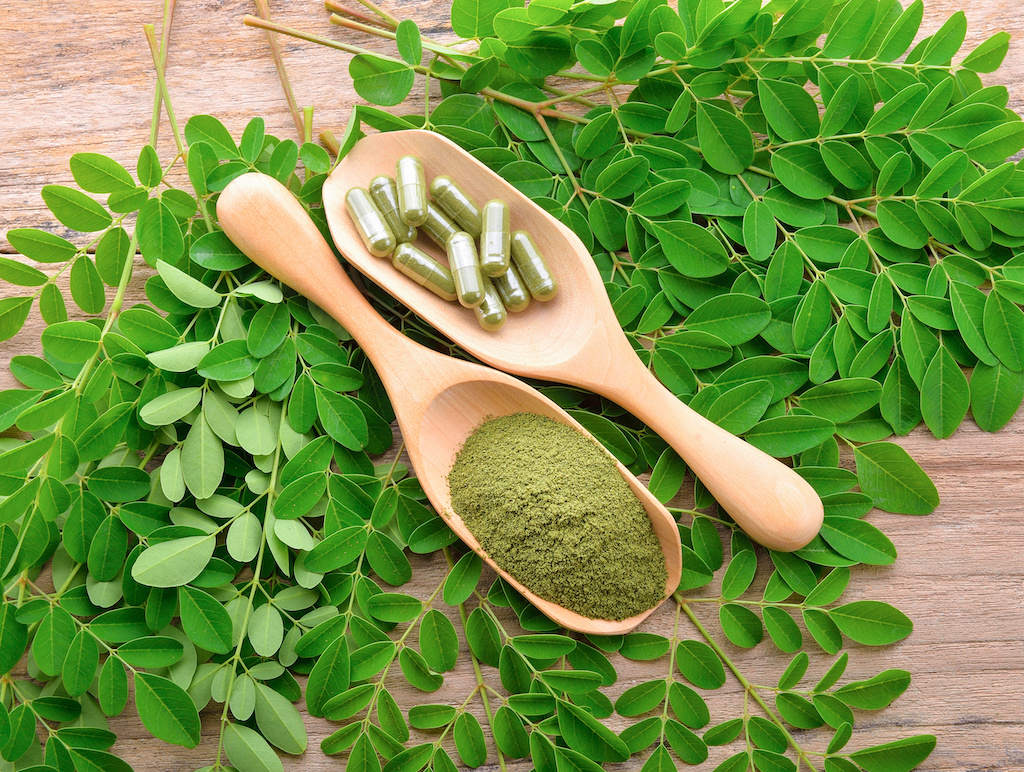
Moringa Capsules are derived from the Moringa plant, which is indigenous to India and various other regions. These capsules are enriched with proteins, vitamins, and minerals, making them a valuable resource in combating malnutrition.
In certain parts of the world, Moringa Capsules have gained significance as a cost-effective and easily cultivated food source. Remarkably, even when dried, Moringa retains a substantial portion of its nutritional content. Furthermore, these capsules possess antioxidant properties, contributing to cellular protection against damage and potentially aiding in reducing inflammation and alleviating discomfort.
Moringa Capsules are employed for various purposes, including managing conditions like asthma and diabetes, as well as supporting breastfeeding, among others. However, it’s important to note that the scientific evidence supporting these applications is currently inconclusive.
Uses & Effectiveness
Moringa Capsules have shown promise in various health-related areas, although the extent of their effectiveness may vary. Here’s a breakdown of some of the potential benefits and areas where research is ongoing:
Asthma: Early studies suggest that a daily intake of 3 grams of Moringa Capsules for three weeks may reduce the severity of asthma symptoms and enhance lung function in adults with mild to moderate asthma.
Diabetes: While the impact of Moringa on diabetes management is still uncertain, initial research indicates that combining Moringa Capsules with sulfonylureas, a type of diabetes medication, may not significantly improve blood sugar control as measured by hemoglobin A1C levels. However, it does appear to reduce fasting and post-meal blood sugar levels when compared to using sulfonylureas alone in diabetes patients. Additionally, Moringa Capsules may potentially lower post-meal blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes who are not on diabetes medications.
HIV/AIDS: Preliminary research suggests that incorporating Moringa Capsules into the daily diet over six months may lead to increased body mass index (BMI) in individuals with HIV/AIDS, although it doesn’t seem to enhance immune function.
High Cholesterol and Lipids: The impact of Moringa on reducing cholesterol levels remains inconclusive, with early, low-quality research yielding mixed results. Further investigation is needed to determine its effectiveness in managing hyperlipidemia.
Breast-Feeding: Studies on the use of Moringa Capsules for boosting breast milk production present mixed findings. Some initial research suggests an increase in milk production after one week of use, while others do not show significant benefits. Long-term usage effects also require further investigation.
Malnutrition: Early research indicates that supplementing children’s diets with Moringa Capsules for two months may help improve weight in malnourished children.
Menopausal Symptoms: In early studies, adding fresh Moringa Capsules to the diet for three months has shown potential in alleviating menopausal symptoms such as hot flashes and sleep disturbances in healthy, postmenopausal women.
Vitamin A Deficiency: Research on adding Moringa Capsules to infant cereal to improve vitamin A levels in infants with deficiency has not yielded positive results.
For various other conditions, such as gum disease, athlete’s foot, birth control, cancer, infections in people with HIV/AIDS, constipation, dandruff, diarrhea, headache, heart disease, heart failure, high blood pressure, sexual desire enhancement, intestinal parasite infections, kidney stones, low red blood cell levels in chronic illness, obesity, osteoarthritis, hyperthyroidism, seizure disorders, skin infections, snakebites, stomach ulcers, gastritis, warts, wound healing, and other ailments, research on the effectiveness of Moringa Capsules is either limited or inconclusive. Further scientific investigation is essential to determine their potential in these areas.
Side Effects of Moringa
Oral Consumption: Moringa Capsules are generally considered safe when the leaves, fruit, and seeds are consumed as part of a regular diet. When used as a short-term medicinal supplement, Moringa leaf and seeds are also likely safe. Products containing Moringa leaf have been used safely for periods of up to 6 months, while those containing Moringa seed have been used for up to 3 weeks. However, it’s important to exercise caution when it comes to Moringa root and root bark, as these parts of the plant may contain toxic substances and are considered potentially unsafe for consumption.
Topical Application: There is insufficient reliable information available to determine the safety of applying Moringa Capsules directly to the skin or to ascertain potential side effects associated with this method of use. Further research is needed to establish the safety profile for topical applications.
Special Precautions and Warnings for Moringa Capsules:
Oral Consumption:
- General: Moringa Capsules are generally considered safe when derived from the leaves, fruit, and seeds and consumed as part of a regular diet. Short-term use of Moringa leaf and seeds as medicinal supplements is possibly safe. Moringa leaf-based products have been used safely for periods of up to 6 months, while those containing Moringa seeds have been used for up to 3 weeks. However, caution is advised with regard to Moringa root and root bark, as they may contain toxic substances and are considered potentially unsafe for consumption.
Topical Application:
- Skin: There is insufficient reliable information available to determine the safety of applying Moringa Capsules directly to the skin or to ascertain potential side effects associated with this method of use. Further research is needed to establish the safety profile for topical applications.
Pregnancy:
- Moringa Leaves: It is possibly safe to use Moringa leaves during pregnancy, particularly during the second or third trimester.
- Moringa Root, Bark, and Flowers: Avoid using Moringa root, bark, or flowers during pregnancy as they may contain chemicals that could potentially induce uterine contractions. Historically, these parts of the Moringa plant were used to cause miscarriages.
Breast-feeding:
- Moringa Leaf: Moringa leaf consumption is possibly safe while breastfeeding for up to 4 months.
- Other Parts of Moringa: There isn’t enough reliable information available to determine the safety of using other parts of the Moringa plant during breastfeeding. To err on the side of caution, it is advisable to avoid their use.
Children:
- Moringa Leaf: Short-term consumption of Moringa leaf is possibly safe for children. It has been used with apparent safety in children for up to 2 months.
It’s essential to exercise caution and consult with a healthcare professional before using Moringa Capsules, especially if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or considering giving them to children. Additionally, if you have any underlying health conditions or concerns, seek guidance from a healthcare provider before incorporating Moringa Capsules into your diet or healthcare regimen.
Dosing Guidelines for Moringa Capsules:
Moringa Capsules are available as dietary supplements and offer a convenient way to incorporate the benefits of Moringa into your daily routine. The dosing recommendations for Moringa Capsules may vary depending on individual needs and specific health conditions. Here are some general guidelines:
- Moringa Capsule Forms: Moringa Capsules are typically available in various forms, such as powders or extracts, which can vary in concentration. Follow the recommended dosage instructions provided on the product label. These instructions may suggest a daily dosage of 6-10 grams by mouth for adults.
- Consult a Healthcare Provider: It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new dietary supplement, including Moringa Capsules. They can provide personalized guidance on the appropriate dosage based on your individual health status, age, and specific health goals.
- Consideration for Specific Conditions: The ideal dosage of Moringa Capsules can differ depending on the health condition you are targeting. Therefore, if you are using Moringa Capsules to address a particular health issue, discuss the dosage with your healthcare provider to ensure it aligns with your treatment plan.
- Monitoring and Adjusting: Pay close attention to how your body responds to Moringa Capsules. If you experience any adverse effects or have concerns about the dosage, consult your healthcare provider for adjustments or further guidance.
- Quality and Source: Ensure you choose a reputable and high-quality source of Moringa Capsules to guarantee product purity and efficacy.
Incorporating Moringa Capsules into your daily routine can be a beneficial way to harness the nutritional advantages of Moringa. However, individual needs and tolerances can vary, so it’s essential to seek professional guidance for the most appropriate and safe dosage for your specific circumstances.